
Types of 1040 Forms and How to Fill Out These 1040 Forms
Commonly referred to as the mother of all tax forms, 1040 is the primary IRS tax form utilized by any United States resident for filing personal federal income tax returns. In this piece, we will explain the 1040 form and how to fill it out for individuals.
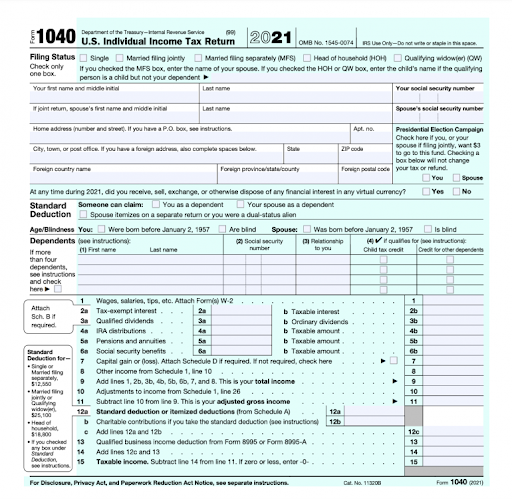
What is a 1040 form?

Officially known as the “U.S. Individual Income Tax Return,” form 1040 is the standard federal tax income form for the people in the United States to file their taxes with the IRS. The 1040 form serves not only to report one’s income but to claim tax deductions/credits and to calculate tax bills or tax refunds for the financial year.
The 1040 form comprises two pages which contain 23 lines (without attachments.) The first page is where one can record personal identification information. The second page contains spaces for you to report income and calculate applicable deductions, credits, figures, and payments made from withheld wages towards the tax liability.
How to Fill Out a 1040 Form?

There are two ways of doing this; you can use tax software like TurboTax, TaxACT, or TaxSlayer, in which case, you can input your information sequentially and print out a complete 1040 form from your computer. The other way is to fill out the form by hand, in which case you can download it from the IRS website.
If you’re looking to learn how to fill out the 1040 form, well, here is a short walkthrough to help you understand the form.
Personal Identification: The first part of the form gathers information about your identity, which tax-filing status you are going for, and the number of tax dependents you have (if applicable.)
Calculate Your Income Taxes: In this section, you may have to sum up all of your income made during the financial year and tally it against any deductions (if applicable.) Undertake this step only if you are confident about your tax bracket; else, seek help from a tax advisor like AOTAX to figure out the details.
Evaluate Your Tax Liability: At the bottom of the form, you will need to fill up the exact amount of income tax you owe the IRS. This stage is where you should deduct any tax credits or prepaid withholdings from your paycheck.
Notify of Any Tax Rebates to the IRS: If you are eligible for a tax rebate using credits or if you have overpaid your taxes, you can fill up your bank details to get a tax refund on your payment.
Pro-tip: If you are an eligible individual who hasn’t received the stimulus check (also known as the Economic Impact Payment), you can get a rebate on your taxes by filling up line 30 on the form 1040. Also, the EIP is not taxable.
What Do You Need to Fill Out the Form 1040?
Okay, here is a list of personal details you should have before filling out the form 1040.
- Social security number for yourself and your dependents (If any).
- Date of birth for yourself and your dependents (If any).
- Statement of wages from your employer and statements of interest or 1099-DIV forms for dividends from banks or brokerages (If applicable.)
- Proof of any tax credits or tax deductions.
- A copy of your previous year’s taxes.
- Your bank account number and routing number (for tax rebates.)
Check out the most effective ways to overcome the problems of filing as a sole proprietor here.
Form 1040 Schedules, What Are They?
There are various schedules for the form 1040 for individuals from varied financial backgrounds. If your financials meet any requirements mentioned below, you may have to add these schedules to your form 1040.
Schedule-1: For individuals with additional income or adjustments to income
Add this schedule if you have any of the following sources or adjustments to your income.
- Business income (you also need to file Schedule C).
- Farm income.
- Rental income (you also need to file Schedule E).
- Deductible health insurance expenses.
- Alimony income or payments.
- Educator expenses.
- Student loan interest.
- Unemployment income.
- Deductible retirement contributions.
- Deductible moving expenses.
- The health savings account deduction.
Schedule-2: Added taxes
You are required to add this schedule if you incur any of the following.
- Household employment taxes.
- Alternative minimum tax.
- Self-employment tax.
- Net investment income tax.
- Repayment of the first-time homebuyer credit.
- Individuals with excess premium tax credit repayments.
- Additional Medicare tax.
- Additional taxes on retirement plans, IRAs, or other tax-favored accounts.
Schedule-3: Additional payments and credits
Most business owners and other individuals with unique financial backgrounds would need to add this to their form 1040.
- General business credit.
- Credit for child and dependent care expenses.
- Foreign tax credit.
- Education credits.
- Retirement savings contributions credit (Also known as the saver’s credit.)
Here Are Some Other Types of Form 1040s You Should Know
While the standard 1040 form is suitable for most individuals, it’s a good idea to learn a few other forms that can come in handy.
Form 1040-V
Form 1040-V is for those who wish to pay the IRS through the mail rather than electronically. It is also commonly known as the payment voucher.
Form 1040-X
The 1040-X is known as the amendment tax return; this form is helpful if you have missed out on reporting any additional income or made a mistake with your first filing.
Form 1040-SR
Designed for people above 60, the 1040-SR is functionally the same while being different aesthetically to help seniors process it comfortably.
Form 1040-ES
The 1040-ES form is best suited for freelance and contract workers who calculate estimated quarterly taxes. It also is helpful for individuals who earn dividends and interest which are not subjected to traditional withholding.
Form 1040-NR
The 1040-NR is suitable for non-residential aliens who engage in business/invest in the US.
With that, we hope that you now have a better idea of the types of 1040s and how to fill out the 1040 form for the IRS. You can relinquish all these complicated steps with just a few clicks to AOTAX! Visit us today by clicking here and get your free tax draft in just 24 hours.
While you are here, learn more about the 12 tax credits and deductions you could be eligible for here.





Recent Comments